为什么开始这个系列
使用Apache Spark多年,但是还是不敢讲精通二字,充其量只是熟练使用的程度。而且它的代码活跃度也很高,发展速度很快,日均能有60个commit。一段时间不学习,可能就会错过很多信息。
如果是以前学习起来这种大型项目,肯定非常花费时间,但是有了LLM后,会大大的提高源码阅读效率。记录一下我用LLM学习它源码的过程。
准备问题
Determine the questions number
My prompt:
one guy said he is a master of Apache Spark, i want to ask him some questions to prove it. Base on the size/complex of Apache Spark project, how many questions do you think is good to prove that? give me the question number and explain the reason.
LLMs’ answers:
| LLM | Answer |
|---|---|
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | … For a solid assessment of “Mastery”: Aim for 10-15 in-depth questions. … |
| GPT 4.1 in Github Copilot | For a project as large and complex as Apache Spark, 5 to 8 well-crafted questions are generally sufficient to assess whether someone is truly a “master” of the technology …. |
| DeepSeek R1 | …. 12–15 well-crafted questions covering core concepts, optimization, troubleshooting, and real-world use cases are ideal. Fewer than 10 may leave gaps, while 15 ensures comprehensive coverage of Spark’s complexity. |
看起来都比较推荐10到15个问题,既然是学习,我们稍微多些就15个吧。
ask LLM prepare the questions
My prompt:
I want to be a master of Apache Spark by reading its source code. Due to this project's extensive capabilities and complexity, learning it with some questions is a good approach. Please help me design 15 well-crafted question. The target is if these questions are answered perfectly, it can be prove that i have been a master of Apache Spark.
同样的,问一下Gemini 2.5 pro / GPT 4.1 / DeepSeek R1, 得到3个答案后,加上my prompt 保存到文件 test.md 里面,让DeepSeek R1 进行总结。Prompt 如下:
I use same prompt to ask Gemini 2.5 pro / GPT 4.1 / DeepSeek R1 then get three version of answer. My prompt and their answers are in the test.md file, read it carefully. My final purpose is list in my prompt, please help combine these three version's answer / delete duplications / structure the questions and other you think is good for my final purpose, then come out a final version. For the final version, you can output more than 15 questions.
最终答案如下,共包含 13 个大类,每个大类下包含 2-3 个问题,总计 25 个问题:
Here's a synthesized and organized list of 25 key questions, combining the strengths of all three versions while eliminating redundancy and grouping by logical themes:
---
### **Core Architecture & Initialization**
1. **Trace SparkContext initialization**: What key components (DAGScheduler, TaskScheduler, SchedulerBackend) are created, and how do they interact with cluster managers (YARN/Kubernetes/Standalone)?
*Key files:* `SparkContext.scala`, `SparkSession.scala`
2. **Spark's execution model**: How does the DAG scheduler split jobs into stages using shuffle dependencies? Explain stage boundary determination.
*Key files:* `DAGScheduler.scala`, `ShuffleDependency.scala`
---
### **RDDs & Data Abstractions**
3. **RDD lineage implementation**: How do transformations (map/filter/join) create lineage chains? Compare narrow vs wide dependencies in code.
*Key files:* `RDD.scala`, `Dependency.scala`
4. **Dataset/DataFrame internals**: How do Encoders bridge JVM objects to Tungsten's memory format?
*Key classes:* `ExpressionEncoder`, `RowEncoder`
---
### **Scheduling & Execution**
5. **Task lifecycle**: Trace a task's journey from DAGScheduler submission to Executor execution (including TaskRunner and BlockManager interaction).
*Key files:* `TaskScheduler.scala`, `Executor.scala`
6. **Locality-aware scheduling**: How does Spark prioritize process-local > node-local > rack-local tasks?
*Key logic:* `TaskSetManager.scala`
---
### **Shuffle & Data Exchange**
7. **Shuffle implementation**: Compare SortShuffleManager vs BypassMergeSortShuffleManager. How do ShuffleWriter/ShuffleReader handle data?
*Key files:* `ShuffleManager.scala`, `IndexShuffleBlockResolver.scala`
8. **Shuffle optimization**: How does Tungsten's UnsafeShuffleManager improve performance through off-heap memory and cache-aware sorting?
---
### **Catalyst & Tungsten Engine**
9. **Catalyst optimization phases**: Trace a query through analysis, logical optimization (e.g., predicate pushdown), physical planning, and code generation.
*Key files:* `RuleExecutor.scala`, `QueryExecution.scala`
10. **Whole-stage codegen**: How does WholeStageCodegenExec collapse operator trees into single functions?
*Key files:* `WholeStageCodegenExec.scala`, `CodeGenerator.scala`
---
### **Memory Management**
11. **Unified memory model**: How does Spark balance execution vs storage memory? Trace spill-to-disk logic in ExternalSorter.
*Key classes:* `UnifiedMemoryManager`, `MemoryStore`
12. **Tungsten memory format**: How does UnsafeRow optimize serialization/deserialization? Compare to Java object overhead.
---
### **Fault Tolerance**
13. **Lineage vs checkpointing**: How does RDD recomputation work? When does lineage truncation occur in Structured Streaming?
*Key logic:* `RDD.checkpoint()`, `HDFSBackedStateStore`
14. **Shuffle fault recovery**: How do MapOutputTracker and BlockManager handle lost shuffle data during executor failures?
---
### **Structured Streaming**
15. **Micro-batch execution**: How does IncrementalExecution transform streaming queries into batches?
*Key classes:* `MicroBatchExecution`, `StreamingQueryManager`
16. **State management**: How does HDFSBackedStateStore implement versioned key-value storage?
---
### **APIs & Extensions**
17. **DataSource V2 API**: How do custom connectors implement batch/streaming reads?
*Key interfaces:* `TableProvider`, `ScanBuilder`
18. **UDF execution**: How are Python/R UDFs integrated via Arrow serialization?
*Key files:* `PythonUDFRunner.scala`, `ArrowUtils.scala`
---
### **Cluster Management**
19. **Dynamic allocation**: How does ExecutorAllocationManager scale resources based on task backlog?
*Key logic:* `ExecutorAllocationManager.scala`
20. **Cluster manager integration**: Compare CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend implementations for YARN vs Kubernetes.
---
### **Advanced Optimization**
21. **Adaptive Query Execution**: How does AQE optimize runtime plan using shuffle statistics (Spark 3+)?
*Key classes:* `AdaptiveSparkPlanExec`, `QueryStage`
22. **Join optimization**: Compare BroadcastJoin vs SortMergeJoin strategies. How is broadcast threshold determined?
*Key logic:* `JoinSelection.scala`, `BroadcastExchangeExec.scala`
23. **Skew handling**: Implement salting technique by modifying CustomPartitioner and AQE configurations.
---
### **Debugging & Observability**
24. **Spark UI architecture**: How do listeners (e.g., LiveListenerBus) collect metrics for web UI?
*Key files:* `SparkUI.scala`, `LiveEntity.scala`
25. **Diagnostic tools**: Use EventLoggingListener and HistoryServer to analyze performance bottlenecks.
---
### **Study Methodology**
- **Code Tracing**: Start with simple flows (e.g., word count) through `SparkContext.runJob()`
- **Debugging**: Set breakpoints in `DAGScheduler.handleJobSubmitted()` and `Executor.TaskRunner.run()`
- **Performance Analysis**: Use `SparkListener` events to track shuffle write/read metrics
- **Contribution Path**: Begin with test coverage in `*Suite.scala` files before modifying core logic
This structure progresses from foundational concepts to advanced optimizations, combining implementation details from all three sources while maintaining logical flow. Each question requires diving into specific subsystems and cross-referencing architectural documentation.
开始学习吧,把这些问题搞明白!
附上几个LLM的回答
直接放到Github Gist上了:https://gist.github.com/waltyou/575021afe2e8d2be0b59656e0e0f7a8d
配置本地运行环境
1. 下载源代码和checkout 版本
git clone https://github.com/apache/spark.git
git checkout tags/v3.5.5
因为 Spark 发展的很快,为了保持一致,这个系列都基于当前(2025-05-15)的最新版本3.5.5.
2. build
follow this: docs/building-spark.md 或者参考我之前写的一篇文章。
the issues i met and solutions
我本地环境是 JDK 17, Windows 11.
- 运行
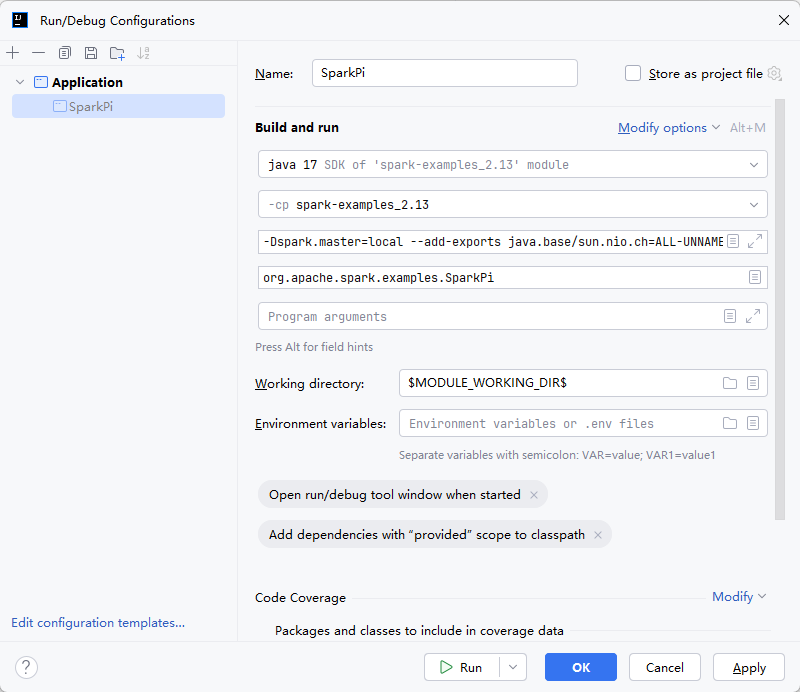
./build/mvn: 用git bash运行,powershell无法运行这个命令 - package sun.misc does not exist: just disable
Use '--release' option for cross-compilationin Java Compiler settings. More details in stackoverflow - class org.apache.spark.storage.storageutils$ cannot access class sun.nio.ch.directbuffer: Add the JVM option “–add-exports java.base/sun.nio.ch=ALL-UNNAMED” in Run Configuration. More details in stackoverflow
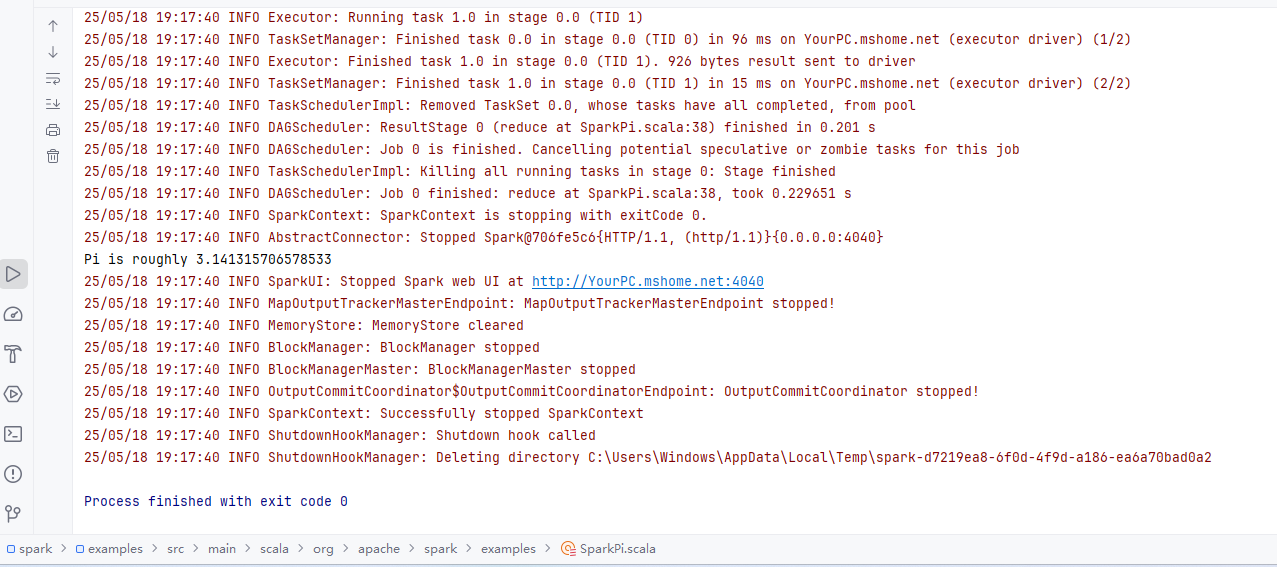
3. Run SparkPi in example module
问题的答案链接
核心架构与初始化
- 问题 01・一、核心架构 ・ SparkContext 初始化链路(DAGScheduler/TaskScheduler 与集群管理器交互)
- 问题 02・一、核心架构 ・ DAG 调度器作业划分逻辑(Stage 边界与 Shuffle 依赖解析)
RDD 与数据抽象
stay tuned…